Making the Smart Move: Integrating AI into QA
by Beatriz Martinho, Software Quality Assurance Engineer
The IT world, as we all know, has utterly transformed. It’s no longer a marathon; it’s a relentless sprint, demanding rapid deliveries and flawless quality. For us in Quality Assurance (QA), this means constant pressure to get things right, and fast.
You’ve surely noticed Artificial Intelligence (AI) making huge waves everywhere. It’s not just hype; AI is genuinely transforming how businesses operate. For QA professionals, that’s genuinely exciting. The core idea? Leveraging AI to dramatically slash time across various QA processes, not just test execution, but crucial upfront work like writing test cases and automating them efficiently.
Imagine: quicker cycles for these fundamental tasks mean we can push out features and products at a far quicker pace, all without ever compromising that vital standard of quality. While the promise of AI in QA is huge, figuring out how to truly integrate it into every single phase of our daily work is still a puzzle we’re actively trying to piece together.
How AI is Reshaping our Approach to QA
1.Requirement Analysis: AI as Your Early Warning System
Starting testing as early as possible is crucial; catching bugs while they’re still in the conceptual phase saves wasted development effort down the line. That’s why getting the QA team involved right from the requirements specification stage is so vital – we can spot those specification flaws before any code is even written.
This is where AI, specifically Large Language Models (LLMs), can be a game-changer. These intelligent systems can analyze your requirements, sifting through them to pinpoint missing information, discrepancies, and inconsistencies that might otherwise slip through. Think of it as having an extra, highly diligent pair of eyes catching potential issues long before they become costly development or testing blockers.
2. Test Case Specification: AI for Comprehensive Coverage
Correct test case specification is essential to ensure subsequent phases run smoothly. It’s often challenging, and extremely time-consuming, to envision every possible scenario, covering both happy and unhappy paths, and document them thoroughly.
This is precisely where LLMs can make a significant impact. LLMs can analyze your project requirements and then generate a comprehensive set of test cases, whether you’re planning for manual testing or automation. They’re capable of thinking beyond the obvious, helping you cover more ground. For automation, an intelligent agent, fed with the context of your project, can generate Cucumber scenarios and even reuse existing steps to ensure consistency and efficiency.
3. Automated Test Implementation: AI as Your Coding Partner
For Test Automation Engineers, writing code is often one of the most demanding tasks. It involves developing robust, maintainable, and adaptable scripts. This typically includes handling repetitive routine code, intricate logic, and persistent debugging.
Fortunately, AI can significantly streamline this effort and enhance code quality. Intelligent agents and AI-powered chats can generate code based on prompts, provide smart auto-completion tips, and analyze existing code to offer feedback with suggestions for improvement.
4. Self-Healing Tests: The Core of AI for Maintenance
Traditional automated tests rely heavily on fixed locators to identify UI elements. When developers change these locators (even subtly), existing tests break. This leads to high maintenance overhead, flakiness, and reduced trust in automation.
This challenge is precisely where AI-powered self-healing mechanisms provide a revolutionary solution. Instead of being confined to static properties, these intelligent systems operate by understanding the broader context and underlying intent of UI elements. Leveraging sophisticated algorithms, AI identifies UI elements not just through a single, brittle attribute, but by analyzing multiple characteristics, their relationships to surrounding elements, and their historical patterns, allowing tests to dynamically adapt to changes and significantly reduce maintenance efforts.
5. Data Generation: AI for Smarter Test Data
Having a complete dataset that accurately simulates a wide range of real-world scenarios, including critical edge cases, boundary conditions, and invalid data, is essential for streamlined testing and ensuring proper coverage. Due to privacy and security concerns, using real production data is often not an option; instead, generating synthetic data becomes a necessity. However, this process of creating synthetic test data can be incredibly time-consuming and repetitive.
With an appropriate prompt, AI can swiftly generate new synthetic datasets that ensure comprehensive coverage, or even effectively uniformize existing data to meet specific testing requirements.
6. Bug Reporting: AI for Precision and Speed
Writing complete and accurate bug reports is absolutely crucial for ensuring defects get fixed swiftly and precisely. However, for many QA professionals, this essential task often becomes a time-consuming, repetitive chore. It’s not just about identifying a bug; it’s about meticulously collecting every relevant detail—reproduction steps, environment information, and ensuring the report is unambiguous enough for developers to act on without constant back-and-forth.
Fortunately, AI can significantly simplify this process. AI-powered tools can assist in numerous ways: from detailing reproduction steps and outlining actual versus expected results, to suggesting severity and priority based on context. They can even review reports for completeness and clarity. By analyzing data like HTTP responses, crash logs, stack traces, and user actions, these tools help construct a thorough narrative and highlight potential root causes, ultimately leading to more efficient bug resolution.
7. Analytics and Reporting: Unlocking Deeper Insights with AI
Beyond just writing and executing test cases, a crucial part of QA involves creating comprehensive reports and deriving actionable insights from collected data. These reports are essential for sharing with development teams, management, and stakeholders, allowing them to analyze trends, grasp underlying patterns, and subsequently plan and adapt strategies with greater precision.
AI possesses the capability not only of automating the generation of detailed reports with various charts, but also of intelligently processing and analyzing the data to automatically draw important conclusions and identify crucial patterns, transforming raw information into strategic intelligence.
Embracing AI as a Force Multiplier for QA
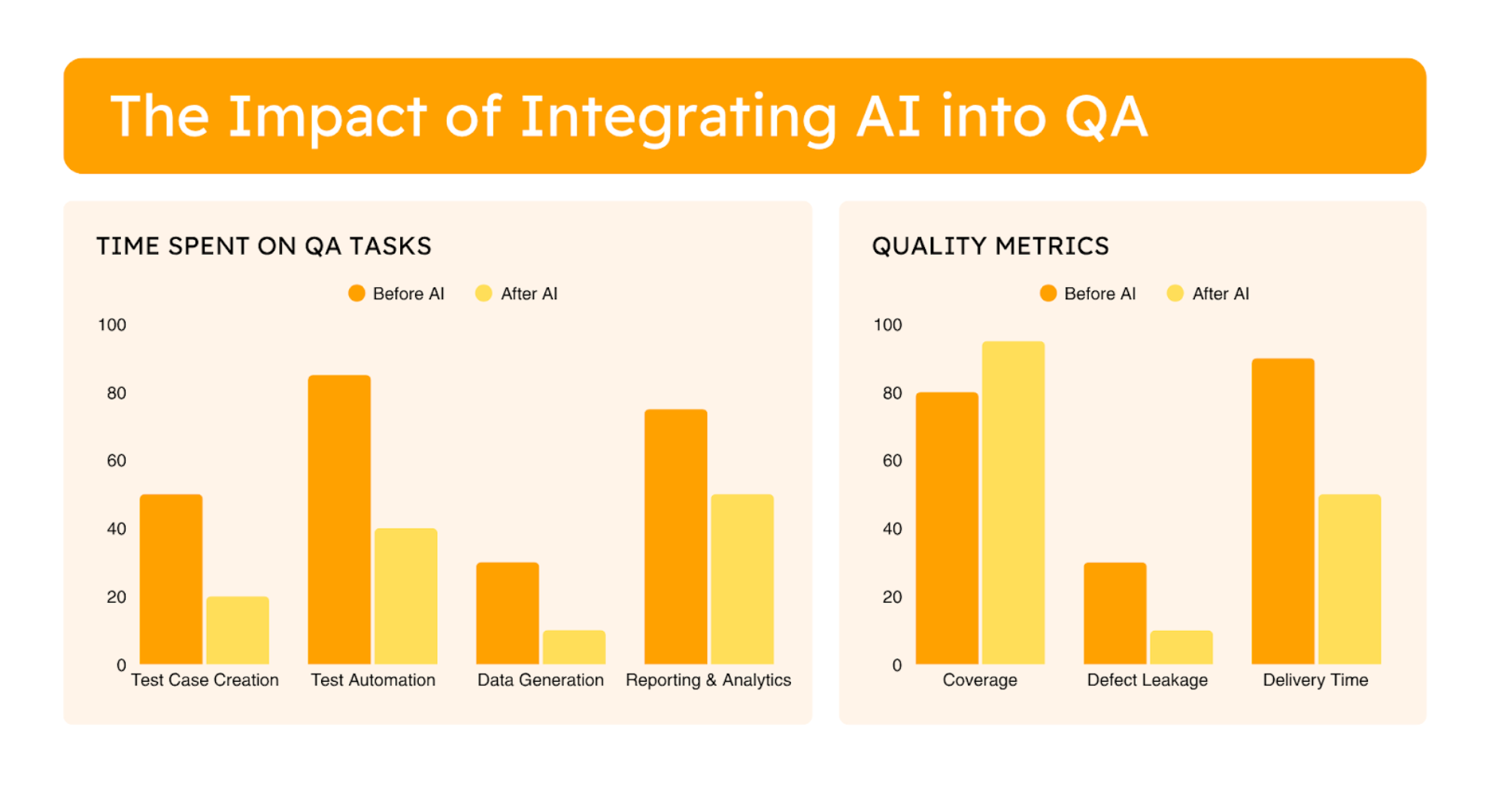
As we’ve explored, Artificial Intelligence isn’t just a buzzword; it’s genuinely shaking things up in QA. From streamlining the test specification process, to enhancing the precision and speed of bug reporting, revolutionizing test maintenance with self-healing capabilities, and providing deeper insights through advanced analytics, AI can do it all. It can significantly boost productivity and efficiency, automating many of the repetitive and time-consuming tasks that often burden QA professionals. This automation, in turn, frees up valuable human time and expertise, allowing teams to dive into more critical, complex, and strategic activities that really require a human touch, ultimately accelerating software delivery cycles.
However, it is crucial to approach this technological evolution with a balanced perspective. AI is incredibly powerful, but it’s not infallible. And crucially, it’s not here to take over our roles as QA professionals. Instead, it serves as a force multiplier that amplifies our capabilities, making us more effective than ever before. So, for any QA team looking to not just keep pace, but truly thrive in the modern software landscape, incorporating AI into our daily workflow isn’t merely an advantage; it’s quickly becoming an essential move. Embracing AI is about empowering QA professionals to achieve new levels of quality and efficiency, ensuring faster, more reliable software for everyone.
Are you already integrating AI into your QA processes? Where do you see your team making the first move?
Related Posts
Comments are closed.